Update: July 5, 2024
Fukuda Method versus Tsuji Method
A unique and interesting new interview with Dr. Junji Fukuda (h/t “Theo”). He discusses in detail the difference between his team’s hair multiplication method versus Dr. Takashi Tsuji’s team’s approach. Dr. Fukuda’s work is being undertaken via a company called TrichoSeeds. Dr. Tsuji’s work is being undertaken via OrganTech.
Dr. Fukuda mentions how the pioneer of hair transplantation (he probably means Dr. Shoji Okuda) is Japanese and one of the pioneers of hair regenerative medicine (Dr. Tsuji) is also Japanese. Shiseido (Japan) could end up also being a pioneer in the hair loss world.
Key quote:
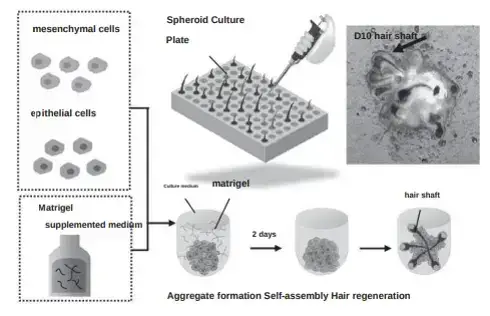
“Dr. Tsuji and his team first extracted hair follicles and increased the epithelial and mesenchymal cells. We did the same thing up to this point. After that, Professor Tsuji and his team created individual hair follicle primordia by massing each type of cell in a centrifuge and combining them under a microscope. We took the approach of mixing epithelial cells and mesenchymal cells extracted from hair follicles in a culture solution and culturing them together.”
He also mentions that when fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) was added to the base medium of Fukuda culture, the efficiency of hair regeneration was significantly increased.
Finally, he mentions the potential cancer side effect that prevents his team from easily creating hair follicles from iPS cells. Japanese laws governing regenerative medicine would allow the use of iPS cells in regenerating vital organs, but not for regenerating hair.
Update: April 18, 2024
New Junji Fukuda interview given to Tokyo Television. Someone please translate if you know Japanese.

February 21, 2024
I have covered the work of esteemed and prolific Japanese hair loss researcher Dr. Junji Fukuda for almost ten years. I also wrote the below two detailed posts about his findings. The second of these is very lengthy because I have kept updating it for a few years.
Make sure to check out the Yokohama National University based Fukuda Lab’s hair research page.
A Visit to Fukuda Lab at Yokohama National
Reader “Theo” just sent me a link to a very interesting diary of a hair transplant surgeon from Japan who just visited the Fukuda Lab.
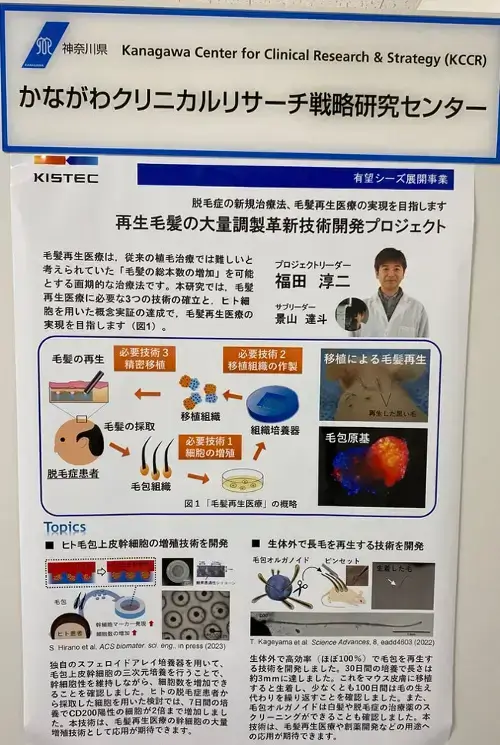
Note that while Dr. Fukuda is based at Yokohama National University, the research seems to be taking place at Kanagawa Life Innovation Center (per the above link). One of the images also mentions the Kanagawa Center for Clinical Research & Strategy (KCCR). Yokohama is the second largest city in Japan and is the capital of Kanagawa Prefecture. Check out this PDF of the regenerative medicine sector at Kanagawa Prefecture.
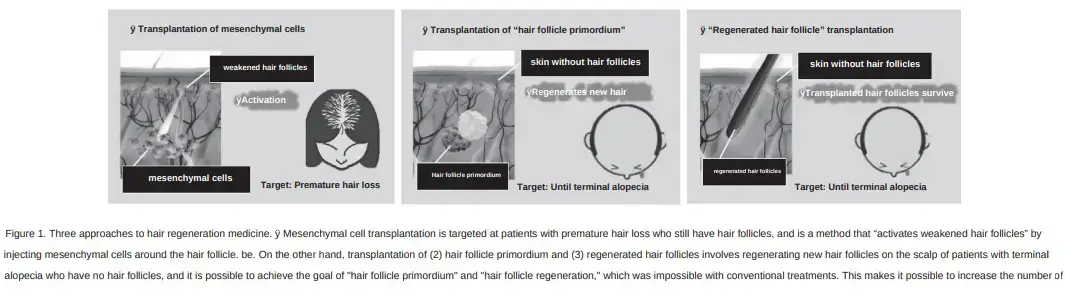
From this visit and summary, I learn some very interesting things. There are three distinct methods in which Dr. Fukuda is pursuing hair regeneration. I mentioned them in my past lengthy post too, but now we have more clarity.
1) Dermal Papilla Cell Transplantation
“Dermal papilla cell transplantation is about to begin in Japan.“
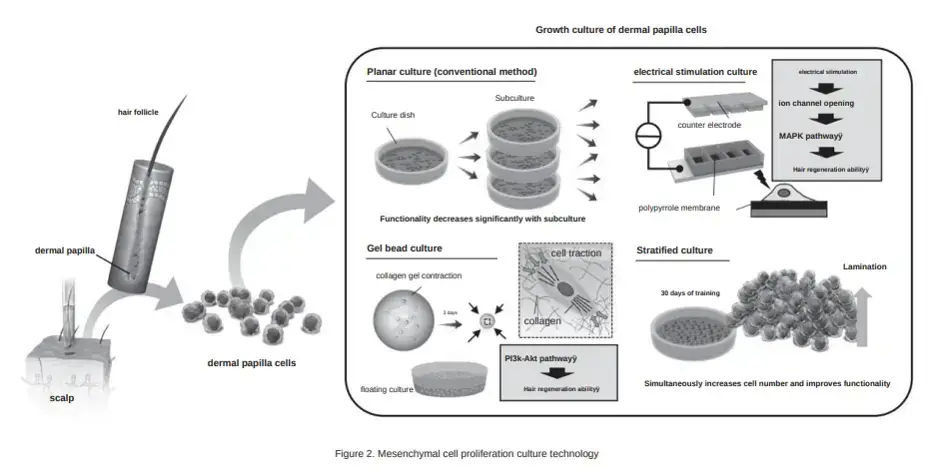
Transplantation of dermal papilla cells (via stratified culture). I assume that the “stratified cuture” in the translation means 3D culturing. Dr. Fukuda mentions that Shiseido already conducted a clinical trial using 2D culturing. In this method, cells are are lined up on a flat surface when culturing, but it only resulted in a 5% increase in hair volume. The 3D method will likely be superior and the clinical trials are about to finally begin! It is hoped to be “put into practical use within five years”.
2) Transplantation of Hair Follicle Primordium
“I think this will take some time.”
The creation of hair follicle primordia means generating hair from scratch. i.e., hair multiplication. I previously discussed the Yokohama team’s process of achieving this via increasing and mixing epithelial cells and mesenchymal cells. These then form “hair follicle primordia“ that are transplanted to the same donor’s scalp in order to regenerate hair in thinning regions of the scalp.
Per the latest feedback from Dr. Fukuda, while this process has already been proven by them in mice, human hair is a different animal. Once the primordium tissue is transplanted to human heads, the direction and length grow haphazardly. He thinks that this will take some time.
3) Transplantation of Regenerated Hair Follicles in Vitro (Organoids)
“It will likely take more than 10 years before it can be used in humans.”
The final method is in vitro regenerated hair follicle transplantation (also called organoid). In this process, hair follicles are regenerated outside the body, lengthened by almost 100%, and then transplanted into the scalp. Per Dr. Fukuda, it will likely take more than 10 years before it can be used in humans.
Other Notes
In March 2023, Dr. Fukuda and his Yokohama team published an important hair regeneration related study. They made an improvement in the expansion of hair follicle stem cells (HFSCs) and dermal papilla cells via the use of a newly designed microwell array device.
The Fukuda Lab has even undertaken research on electric stimulation of human dermal papilla cells for hair regeneration.
So in one day we get two very unique insights and forecasts from Japan! Thanks again to “Theo” for all the stellar non-English language updates from Japan and South Korea.
Naohiro Uchida, Director of Almo Plastic Clinic Hair Transplantation.