My favorite vitamin D (which is actually a hormone) supplement is this oil. Each drop contains 2,000 IU, so be careful to not overdose. I rarely recommend any product so highly, but this one quickly raised my vitamin D levels to the desired number. Having said that, my hair loss did not stop even after this supplementation.
Vitamin D and Hair Loss
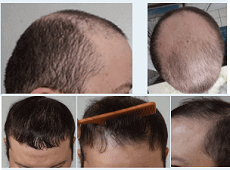
Update: August 2022 — Dr. Sharon Keene just released an incredible case report of a severely vitamin D deficient patient. More here. His vitamin D value was just 12ng/ml, which is also around my level when I do not supplement. This patient regrew significant hair after completing a 6-week course of weekly dosing of 50,000 IU vitamin D3; followed by 10,000 IU/week for 8 months.
I often stop taking my own Vitamin D supplement for up to a month, and it might even be expired or damaged (I store it outside). After reading this report, I plan to purchase a new bottle this winter and adhere more closely to the recommended treatment protocol.
Update: July 2020 — Turkish scientists found that mean serum ferritin and 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels were significantly lower in patients with hair loss.
Update: June 2020 — A new study from India found that 86 percent of men with androgenetic alopecia (male pattern hair loss) had low vitamin D levels.
July 31, 2017
Vitamin D deficiency has been blamed for hair loss in select cases. Usually, this type of hair loss is temporary. Some researchers believe that vitamin D supplementation can reverse hair fall and lead to hair regrowth in select cases. One recent study concluded that:
“Lower expression of CYP27B1 in patients with AGA supports the notion that changes in vitamin D metabolism contributes to hair loss.”
The role of vitamins and minerals (such as Biotin and B-12) in hair loss is important. During the past decade, vitamin D has been in the news more so than any other vitamin. Its deficiency has been touted as the reason for dozens of human health problems. These include rickets, osteoporosis, teeth loss, depression, cancer, high blood pressure and multiple sclerosis.
Deficiency
For most such health related problems, there is insufficient evidence that a vitamin D deficiency caused the condition in the first place. Nor is there concrete evidence that vitamin D supplementation causes any significant improvements in most such health problems.

Having said that, there are some conditions (e.g., rickets and other bone problems) where prolonged vitamin D deficiency has been proven to have a strong causative effect.
And there exist a number of other conditions where there is some evidence of the importance of a sufficient intake of vitamin D. After all, most plants and animals need direct sunshine (which generates vitamin D) in order to thrive.
As is the case with most vitamins and minerals, deficiencies are usually far more dangerous in early childhood than in adulthood. Initial symptoms of vitamin D deficiency include fatigue, mood changes, and bone and muscle weakness.
Types of Vitamin D
There are five types of vitamin D, known simply as D1, D2, D3, D4 and D5. Of these five, the two major forms are D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol). When doctors talk about vitamin D, they generally mean D2 or D3 or both (collectively referred to as calciferol). D3 is generally preferred over D2.
Direct sunlight exposure is the easiest way to raise one’s vitamin D levels. The skin synthesizes vitamin D upon exposure to ultraviolet rays (US). Darker skinned individuals require longer exposure times to sunlight than lighter skinned individuals, in order to garner similar benefits.
Numerous food items naturally contain vitamin D. Many are artificially enhanced with the addition of D2 or D3, especially in developed countries. The US FDA allows up to 84 IU/100g of Vitamin D3 addition in milk; and up to 84 IU/100g of Vitamin D2 addition in yogurt. Both males and females required similar levels of this crucial vitamin.
Optimal Vitamin D Levels
Modern life is heavily indoor-focused. Daytime computer based work is followed by entertainment and social media related screen-time in the evenings for most people. Not to mention 24/7 smartphone access, usually indoors or in shady areas in order to avoid sun glare. This has drastically reduced direct sunlight exposure in just one generation. Sunlight has historically been the best way for most of us to get our daily vitamin D.
Moreover, daily warnings about skin cancer and skin aging have meant that even when outdoors, most people lather on sunscreen and suntan lotion. This drastically limits vitamin D synthesis via the skin. Moreover, if you are mostly getting your daily sunshine through office windows or car windows, it does not raise your levels either. Glass prevents UV rays from synthesizing D vitamins on your skin.

Because of all the above, most readers must have heard a lot in recent years about the huge number of people who are vitamin D deficient and the potential dangers of this problem. In fact in a radio show just last week, I heard that some scientists think that the current cutoff levels are too low, and if corrected, around 80 percent of Americans are vitamin D deficient (although this is a controversial issue). Quite often, people who are warning about this issue are also selling vitamin D supplements. So one must be vary about the messenger.
There is significant debate about:
- Ideal levels of vitamin D (i.e., what number seems to be the best for overall health).
- Insufficient levels of vitamin D (i.e., below what number does it become dangerous for your health).
The most common measurement for vitamin D levels is done via a blood test known 25-hydroxyvitamin D, with resulting numbers given in ng/mL. For those outside the US, just multiply these numbers by 2.5 to get corresponding numbers in nmol/L.
Most doctors consider that levels below 20 ng/mL are insufficient. Many nowadays have raised this number and consider levels below 30 ng/mL to be insufficient.

Ideal levels are even more heavily debated, with some data suggesting as high as 70 ng/mL. Other data suggests that anything over 50 ng/mL can be dangerous if consistently that high. Yet other data suggests that anything over 30 ng/mL does not lead to any benefits.
Trying to analyze the 100 plus studies on this subject matter would be way beyond the scope of this blog. Moreover, your genetics, race, sex, height, weight and more can also impact the ideal levels for you.
I am happy if my levels are over 20 ng/mL, which they are not in winters. So I supplement with capsules. If they go really low, I use this oil based liquid product.
Past Research
Over the years, I have read numerous comments from people suggesting that a lack of vitamin D has an undesirable impact on hair loss and growth. Moreover, while researching for this post, I found that even some respected scientists have postulated this theory and a WSJ article in 2012 looked at this subject in detail. No vitamin D deficiency before and after pictures were provided.
- Per the above article, the leading researcher in this field seems to be Dr. Marie Demay, a professor at Harvard Medical School. According to her, the vitamin D receptor (VDR) activates hair growth, rather than the vitamin itself. The Demay Lab continues to do research on the vitamin D receptor and hair growth (plus keratinocyte stem cells). Their latest study related to this subject matter came out in March of 2017, and is titled: “Absence of vitamin D receptor (VDR)-mediated PPARγ suppression causes alopecia in VDR-null mice“. Previously, they covered the role of VDR in hair follicle biology.
- Also important, in 2012, a research team led by Dr. Yuko Oda at UCSF found that knocking out (ablating) the transcriptional coactivator mediator (MED1) in mice led to increased hair growth.
- And finally, a team from Japan led by Dr. Kotaro Yoshimura and Dr. Noriyuki Aoi published an important study in 2012 . It found that 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 (Calcitriol or VD3) promotes functional differentiation of dermal papilla cells (DPCs). This “could be useful in preserving the hair follicle-inductive capacity of cultured DPCs for hair regeneration therapies”. Apparently, this could also help improve hair transplantation results.
- A 2016 study from Egypt found lower serum and tissue VDR levels in patients with AA and AGA. This was in comparison to those with neither form of hair loss.
Other Notes
- Many hair loss products that I have seen over the years have included vitamin D3 as one of the ingredients. I highly doubt that this makes much of a difference in re-growing lost hair despite great before and after photos.
- It should be noted that even if you take vitamin D supplements orally, for many people (including myself), it sometimes requires mega doses (upwards of 20,000 IU per day, at least initially) to have any significant impact on one’s blood test readings. Some doctors will not prescribe that much due to potential side effects, although I do not think this danger has been proven. Some people have tried topical vitamin D for their hair loss.
- I seem to have better hair when I am out in the sun a lot. I am certain this is not psychological. How about you? Like other animals and plants, I think that humans need sufficient levels of sunshine, water and oxygen in order to thrive.
- It is interesting that low-level laser therapy (LLLT) has been shown to benefit hair growth in a number of studies. The average wavelength of light from LLLT devices is in the 600nm-900nm range. UV rays from the sun fall in the 300nm-400nm wavelength range.
- In most scenarios where things such as vitamins, minerals, growth factors and so forth are involved, it seems like women tend to benefit more than men. This is based on my general intuition from what I have read over the years. Male hormones are usually the predominant reason for men’s hair loss. When it comes to hair loss in women, other factors are often more important. I would not be surprised if when vitamin D does benefit hair, it is more effective in women.
- Sunlight also seems to kill mites (e.g., demodex) and improve other scalp problems for many people.
- An interesting study from Hungary suggests that androgenetic alopecia might have been an evolutionary mechanism to protect men from advanced prostate cancer. A bare scalp enhances UV ray absorption into the scalp, and increased UV radiation apparently reduces the risk of prostate cancer. Not sure about this finding. Men who suffer from AGA are more likely to have prostate cancer. So according to this theory, they would be even more likely to have prostate cancer if they had all their hair intact.
- Reddit Tressless often has anecdotal reports on this subject. e.g. Vit D saved me.
Vitamin D Supplements for Hair Loss
I had considered writing this post in the past, but put in on the backburner until I recently got two e-mails from a person I will address as “Mr. BB”. These e-mails entail taking Vitamin D supplements for hair growth. I am pasting most of his two e-mails’ content below:
E-mail 1:
“I found this page and thought it could be of interest for you as you also follow closely the AA. Its dated from February 2017:
https://www.vitamindcouncil. org/new-study-finds- derivative-of-activated- vitamin-d-helps-manage-hair- loss/
I am taking vitamin D3 supplement since 14th of April 2017 and must say that within 3 or 4 days (not weeks or months) I noticed the hair stopped falling. I even think my hair is growing back in some places. The doses I take are important. In fact today I am taking 30000 UI daily.
I started to lose my hair around 1992-1993. It’s been a slow process, but it has reached a level that made me think I’d better shave it all. Until I found some study on D3 and started to supplement myself. I think it is working.
It is already a miracle that something could make your hair loss stop let alone something that makes it regrow and boosts thickness and growth. What if the cure has always been here and it was just of Vitamin D deficiency? In countries in which we live in (Europe, North America), it has been proven that 80 % of population is deficient.
By the way Vitamin D3 is not a Vitamin. It is a Hormone and is said to enter in the expression of about 200 genes among which is the synthesis of a natural antibiotic that fights against the seasonal flu (influenza).”
E-mail 2, after I sent him a brief reply:
“There is something that I have heard about D3 from a specialist who even wrote a book about it.
That guy was saying that they discovered that French are Magnesium Chloride deficient. And guess what? Magnesium Chloride is a cofactor to the vitamin D. Meaning that you they need to go hand in hand if you want to see real benefits. Magnesium Chloride is the key!
I was on Magnesium Chloride since 22nd of March 2017. And taking only that stopped my spring allergy and breathing problems. I am taking about 200 ml of magnesium chloride a day. That is 100 ml after each meal.
Few weeks later as I saw my health was improving I started to also take vitamin C. I dilute about 5 g of vitamin C powder in my 100 ml magnesium preparation.
Than I started vit D on the Easter weekend with just 4000 UI and before the weekend was over I noticed the hair stopped falling.
Note that you can find many studies that suggest a correlation between magnesium levels and vitamin D levels.”