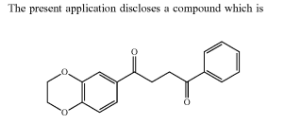
In 2017, I covered the development of a new biochemical peptide material called PTD-DDM that would grow hair. The peptide targets the CXXC5 gene, resulting in activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. This is turn leads to accelerated hair regrowth.
The South Korean team that conducted this research was led by Dr. Kang-Yell Choi, who even has a wikipedia entry. I previously also covered Dr. Choi in my post on valproic acid and hair growth.
CK Regeon
To bring this hair growth peptide (KY19382) to market, Dr. Choi started a company named CK Biotech that I mentioned in my original post. However, in 2021, it was renamed to CK Regeon.
Recently, I heard again about this company due its presentation at a June 30, 2022 South Korean symposium on the development of innovative new drugs for hair loss. This conference was led by Epibiotech and Yonsei University. On an interesting side note, Inventage Lab also presented at this conference, indicating that finasteride injections are still on track.
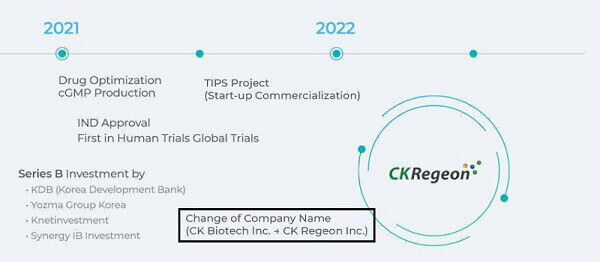
Make sure to read CK Regeon’s regular press releases. On Linkedin, the company currently has 8 employees. On the company’s Twitter page, they keep sharing an updated infographic on the benefits of Wnt pathway activation. The latest heading:
“WNT Pathway restoration, a therapeutic target for tissue regeneration, diabetic wound healing, hair growth, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), obesity and diabetes.”
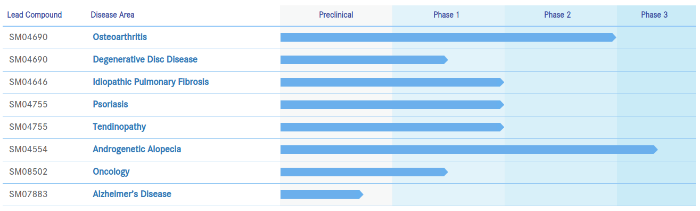
On the company’s target diseases page and pipeline page, they include the above conditions as well as “countering short stature” and treating Alzheimer’s disease.
While I doubt that CK Regeon can cover all these bases, it is not surprising that the Wnt/Beta-Catenin signaling pathway is so crucial to human health.
Blocking CXXC5 and Improved Wnt/Beta-Catenin Signaling
Previously, we got excited about the potential of Samumed in curing hair loss by activating the Wnt pathway. Unfortunately, this company did not pan out after years of favorable publicity.
Another company named Frequency Therapeutics is trying to regrow inner ear hair cells via stimulating the Wnt signaling pathway. Fractional lasers and wounding also work on the same pathway, leading to a regrowth of scalp hair in some who are lucky.
CK Regeon’s overall technology entails blocking the CXXC5-Dishevelled (Dvl) protein-protein interaction (PPI). This is accomplished via the creation of new small molecules or peptides. This inhibition of CXXC5 results in restored Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and hair regrowth.
Note that CXXC5 is overexpressed in men with androgenetic alopecia (aka male pattern baldness). CXXC5 is a negative feedback regulator of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway.